- Example of a Binary Search Tree
[min-max-nodes-ll.png]
[min-max-nodes-balanced.png]
Given a tree, be able to determine the order of each traversal type:
[Number tree]
class BST {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(val, currentNode =
this.root) {
if (!this.root) {
this.root = new
TreeNode(val);
return;
}
if (val < currentNode.val)
{
if (!currentNode.left) {
currentNode.left = new
TreeNode(val);
} else {
this.insert(val,
currentNode.left);
}
} else {
if (!currentNode.right) {
currentNode.right = new
TreeNode(val);
} else {
this.insert(val,
currentNode.right);
}
}
}
}
let matrix = [
/* A B C D E F */
/*A*/
[true, true, true, false, true,
false],
/*B*/
[false, true, false, false,
false, false],
/*C*/
[false, true, true, true, false,
false],
/*D*/
[false, false, false, true,
false, false],
/*E*/
[true, false, false, false,
true, false],
/*F*/
[false, false, false, false,
true, true]
];
Correct Steps
Strategies
Amortized Analysis : Method for analyzing a given algorithm’s complexity, or how
much a resource, especially time or or memory, it takes to execute.If you have seen the problem before, just tell them you have.

GraphNode Class
class GraphNode {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.neighbors = [];
}
}
let a = new
GraphNode("a");
let b = new
GraphNode("b");
let c = new
GraphNode("c");
let d = new
GraphNode("d");
let e = new
GraphNode("e");
let f = new
GraphNode("f");
a.neighbors = [b, c,
e];
c.neighbors = [b, d];
e.neighbors = [a];
f.neighbors = [e];

let matrix = [
/* A B C D E F */
/*A*/ [true, true, true, false, true, false],
/*B*/ [false, true, false, false, false, false],
/*C*/ [false, true, true, true, false, false],
/*D*/ [false, false, false, true, false, false],
/*E*/ [true, false, false, false, true, false],
/*F*/ [false, false, false, false, true, true],
];Traversal with Graph Node Depthfirst Recursion
class GraphNode {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.neighbors = [];
}
}
let a = new GraphNode("a");
let b = new GraphNode("b");
let c = new GraphNode("c");
let d = new GraphNode("d");
let e = new GraphNode("e");
let f = new GraphNode("f");
a.neighbors = [e, c, b];
c.neighbors = [b, d];
e.neighbors = [a];
f.neighbors = [e];function depthFirstRecur(node, visited = new Set()) {
// if this node has already been visited, then return early
if (visited.has(node.val)) return;
// otherwise it hasn't yet been visited,
// so print it's val and mark it as visited.
console.log(node.val);
visited.add(node.val);
// then explore each of its neighbors
node.neighbors.forEach((neighbor) => {
depthFirstRecur(neighbor, visited);
});
}function depthFirstIter(node) {
let visited = new Set();
let stack = [node];
while (stack.length) {
let node = stack.pop();
// if this node has already been visited, then skip this node
if (visited.has(node.val)) continue;
// otherwise it hasn't yet been visited,
// so print it's val and mark it as visited.
console.log(node.val);
visited.add(node.val);
// then add its neighbors to the stack to be explored
stack.push(...node.neighbors);
}
}Traversal with Adjacency List
function depthFirst(graph) {
let visited = new Set();
for (let node in graph) {
_depthFirstRecur(node, graph, visited);
}
}
function _depthFirstRecur(node, graph, visited) {
if (visited.has(node)) return;
console.log(node);
visited.add(node);
graph[node].forEach((neighbor) => {
_depthFirstRecur(neighbor, graph, visited);
});
}
depthFirst(graph);OSI : The Open Systems Interconnection reference model is a well known Network
Model created in the UK that has both conceptual layers and suggested protocols for each.

Application : Includes information used by client-side software, data from this
later interacts directly with applications. (i.e. HTTP)Presentation : The syntax later that converts data from machine-readable to
human-readable. Includes data compression, encryption, and character encoding. (i.e. JPEG & GIF)Session : Includes protocols responsible for authentication and data continuity.
Includes authorization or re-establishing a dropp connection. (i.e. RPC (Remote Procedure Call))Transport : Utilization of transport protocols (i.e. TCP and UDP)Network : Basically the internet layer (i.e. IP)Data Link : Deal with connections from one machine’s network interface to
another. (i.e. ethernet)Physical : Translating raw electrical signals to bits & bytes of data.
(i.e. Wi-Fi & DSL)TCP/IP is much more practical compared to OSI, but it is purely practical.
Reference Model : A High-level overview of a complex topic provided by an
organization that manages it.Layers of the TCP/IP Model
Application : Includes protocols related to user-facing data. Anything that is
transmitted from the Transport layer is considered Application Layer Data (i.e. HTTP & FTP)Transport : TCP & UDP.Internet : Connects separate networks together (IP)Link : Lower-level communication standards.Physical? : There is a supposed fifth layer that cinludes all the electrical
concepts that span across wires, but it is not officially stated. 
Binary : Number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system.
Base : Number System, computers use a Base 2 NS.CPU : Central Processing Unit, an electronic circuitry within a computer that
executes instructions that make up a computer program.
1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128…etc.
Bit : A single digit represented by either 1 (ON) or 2 (OFF). 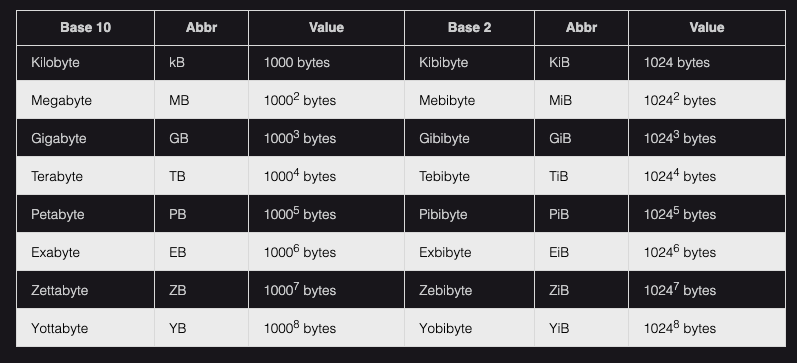
Byte : Sequence of 8 Bits.
Hexadecimal : Base 16, useful numeric system due to it making it easier for us to
read binary.
0x.FF = 255 = 11111111 = 1 bytehexadecimal: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F
decimal: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15
pre data-role="codeBlock" data-info="js" class="language-javascript">Regular Numbers: 4 8 15 16 23 42
Binary: 00000100 00001000 00001111 00010000 00010111 00101010
Hexadecimal: 04 08 0F 10 17 2A
TCP : Transmission Control Protocol.
IP : Internet Protocol.Internet : A series of interconnected networks sharing data.Packet : Format that IP data is packaged in.
Pack-Switching : When a message is split up into separate ‘packets’, delivered to a
destination, and reassembled as appropriate. > A Byte is 8 Bits >
IPv4 is still the most commonly used protocol version online.

Version : Binary representation of the version #.Traffic Class : Used to Identify different types of packets.Flow Label : An experimental option used for adding packet sequencing into IP.Payload Length : Let’s the receivers know how large the data in the packet will be.
Next Header : Usually identifies the protocol type of the packet’s data.Hop Limit : Means of preventing packets from being passed around routers forever.
Source Address : Where the pack originated.Destination Address : Where the packet is heading. > All of the headers have a
fixed length of 40 bytes.Special Addresses
127.0.0.10.0.0.0Port : Virtual interfaces that allow a single device to host lot’s of different
applications & services.TCP : Transmission Control Protocol, the most common transport protocol.
UDP : User Datagram Protocol.
DNS : Domain Name System is a distributed appraoch to providing easily-understood
names for internetworked devices. (Similar to a phonebook)
Domain : A website’s domain refers to the ‘friendly’ name for the website’s host, or
the server providing the site’s content. 
Resolution : Process of working out which name server is needed.
DNS Records
Zone File : Text file containing, host names, IP Addresses, and resource types.SOA : Start of Authority, let’s use know what name server is the primary
authority (THE MINIMUM REQUIREMENT IN A ZONE FILE)NS : Keeps us connected to our zone by pointing to name servers.A/AAAA : A = Domain Name to IPv4 & AAAA = Domain Name to IPv6CNAME : Links Domain name to Domain Name.MX : Mail Exchanger, used by e-mail clients.TTL : Time to live, measure of how long a record should be cached by a DNS name
server.HUB : Simplest networking device aka a Signal Splitter.
Flood : If a destination address is unknown, the switch will flood received data
out to all connect devices.Forward : If the destination is known, it will send data directly to that
device.Filter : When data is dropped entirely from a transfer.Routers : Connect separate networks with each other.
it allow us to talk formally about how the runtime of an algorithm grows as the input grows.
n = number of operation the computer has to do can be: f(n) = n f(n) = n^2 f(n) = 1
f(n) = could be something entirely different !

O(n):
function addUpToSimple(n: number) {
let total = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
total += i;
}
return total;
}O(1):
O(n): maybe thinking O(2n) but we see big picture! BigONotation doesn’t care about precision only about general trends linear? quadric? constant?
function printUpAndDown(n: number) {
console.log("Going up");
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
console.log("Going down");
for (let j = n - 1; j > 0; j--) {
console.log(j);
}
}O(n^2)
function printAllPairs(n: number) {
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
console.log(i);
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
console.log(j);
}
}
}O(n) : cuz as soon as n grows complexity grows too
function logAtLeastFive(n: number) {
for (let i = 0; i <= Math.max(5, n); i++) {
console.log(i);
}
}O(1)
Rules of Thumb
O(1)
function sum(arr: number[]) {
let total = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
total += arr[i];
}
}O(n)
function double(arr: number[]) {
const newArr = [];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
array.push(arr[i] * 2);
}
return newArr;
}object:
const person = { name: "John", age: 22, hobbies: ["reading", "sleeping"] };
Object.keys(person); // ["name", "age", "hobbies"] O(n)
Object.values(person); // ["John", 22, Array(2)] O(n)
Object.entries(person); // [Array(2), Array(2), Array(2)] O(n)
person.hasOwnProperty("name"); // true O(1)array: push() and pop() are always faster from unshift() and shift() cuz inserting or removing element from beginning of an array needs reIndexing all elements
O(n^3)
function same(arrOne: number[], arrTwo: number[]): boolean {
if (arrOne.length !== arrTwo.length) {
return false;
}
for (let element of arrOne) {
// for O(n)
if (!arrTwo.includes(element ** 2)) {
// includes cuz iterate over all indexes O(n)
return false;
}
arrTwo.splice(arrTwo.indexOf(element ** 2), 1); // indexOf cuz iterate over all indexes O(n)
}
return true;
}frequencyCounter:
O(n)
function same(arr1: number[], arr2: number[]) {
if (arr1.length !== arr2.length) {
return false;
}
const frequencyCounter1 = {};
const frequencyCounter2 = {};
for (let val of arr1) {
frequencyCounter1[val] = (frequencyCounter1[val] || 0) + 1;
}
for (let val of arr2) {
frequencyCounter2[val] = (frequencyCounter2[val] || 0) + 1;
}
for (let key in frequencyCounter1) {
const sqrtKey = parseInt(key, 10) ** 2;
if (
!(sqrtKey in frequencyCounter2) || // interesting ** in ** check if object contains key
frequencyCounter2[sqrtKey] !== frequencyCounter1[key]
) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}O(n)
// approach one
function validAnagram(str1: string, str2: string): boolean {
if (str1.length !== str2.length) {
return false;
}
const frequencyCount1 = {};
const frequencyCount2 = {};
for (let value of str1) {
frequencyCount1[value] = (frequencyCount1[value] || 0) + 1;
}
for (let value of str2) {
frequencyCount2[value] = (frequencyCount2[value] || 0) + 1;
}
for (let key in frequencyCount1) {
if (frequencyCount1[key] !== frequencyCount2[key]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// approach two
function validAnagram(str1: string, str2: string): boolean {
if (str1.length !== str2.length) {
return false;
}
const frequencyCount = {};
for (let i = 0; i < str1.length; i++) {
const currentElement = str1[i];
frequencyCount[currentElement]
? (frequencyCount[currentElement] += 1)
: (frequencyCount[currentElement] = 1);
}
for (let i = 0; i < str2.length; i++) {
const currentElement = str2[i];
if (!frequencyCount[currentElement]) {
return false;
} else {
frequencyCount[currentElement] -= 1;
}
}
return true;
}O(n^2)
function sumZero(arr: number[]) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] + arr[j] === 0) {
return [arr[i], arr[j]];
}
}
}
}multiple pointers:
O(n)
function sumZero(arr: number[]) {
let left = 0;
let right = arr.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
const sum = arr[left] + arr[right];
if (sum === 0) {
return [arr[left], arr[right]];
} else if (sum > 0) {
right--;
} else {
left++;
}
}
}O(n)
// my approach
function countUniqueValues(arr: number[]): number {
let pointer = 0;
let count = 0;
while (pointer < arr.length) {
if (arr[pointer] === arr[pointer + 1]) {
pointer++;
} else {
count++;
pointer++;
}
}
return count;
}
// steele approach
function countUniqueValues(arr: number[]): number {
if (arr.length === 0) {
return 0;
}
let i = 0;
for (let j = 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] !== arr[j]) {
i++;
arr[i] = arr[j];
}
}
return i + 1;
}O(n^2)
function maxSubArraySum(arr: number[], n: number): number | null {
if (arr.length < n) {
return null;
}
let max = -Infinity;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length - n + 1; i++) {
let tmp = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
tmp += arr[i + j];
}
if (tmp > max) {
max = tmp;
}
}
return max;
}O(n)
sliding window:
function maxSubArraySum(arr: number[], n: number): number | null {
if (arr.length < n) {
return null;
}
let maxSum = 0;
let tmpSum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
maxSum += arr[i];
}
for (let i = n; i < arr.length; i++) {
tmpSum = tmpSum - arr[i - n] + arr[i];
maxSum = Math.max(tmpSum, maxSum);
}
return maxSum;
}linearSearch
O(n)
function linearSearch(arr, val): number {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] === val) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}divide an conquer:
binarySearch
O (Log n)
function binarySearch(sortedArr: number[], value: number): number {
let min = 0;
let max = sortedArr.length - 1;
while (min <= max) {
let middle = Math.floor((min + max) / 2);
if (sortedArr[middle] < value) {
min = middle + 1;
} else if (sortedArr[middle] > value) {
max = middle - 1;
} else {
return middle;
}
}
return -1;
}a process that calls itself
quick note around callStack
function wakeUp() {
// callStack [wakeUp]
takeShower();
eatBreakfast();
console.log("Ready to go ... ");
} // callStack []
function takeShower() {
// callStack [takeShower, wakeUp]
console.log("taking shower");
} // callStack[wakeUp]
function eatBreakfast() {
// callStack [eatBreakfast, wakeUp]
const meal = cookBreakFast();
console.log(`eating ${meal}`);
} // callStack [wakeUp]
function cookBreakFast() {
// callStack [cookBreakFast, eatBreakfast, wakeUp]
const meals = ["Cheese", "Protein Shake", "Coffee"];
return meals[Math.floor(Math.random() * meals.length)]; // callStack [eatBreakFast, wakeUp]
}
wakeUp();two essential part of recursive functions
function sumRange(num: number) {
if (num === 1) return 1;
return num + sumRange(num - 1);
}
function factorial(num: number) {
if (num === 1) return 1;
return num * factorial(num - 1);
}helper method recursion vs pure recursion
// helper method recursion approach
function collectOdd(arr: number[]) {
const result = [];
function helper(helperArr: number[]) {
if (!helperArr.length) {
return;
}
if (helperArr[0] % 2 !== 0) {
result.push(helperArr[0]);
}
helper(helperArr.slice(1));
}
helper(arr);
return result;
}
// pure recursion approach
function collectOdd(arr: number[]): number[] {
let result = [];
if (!arr.length) {
return result;
}
if (arr[0] % 2 !== 0) {
result.push(arr[0]);
}
result = collectOdd(result.concat(arr.slice(1)));
return result;
}indexOf() includes() find() findIndex() all this methods doing linear search behind the scene
O(n)
function linearSearch(arr: number[], value: number): number {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] === value) {
return i;
}
return -1;
}
}O(Log n)
function binarySearch(sortedArr: number[], value: number): number {
let left = 0;
let right = sortedArr.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
const middle = Math.round((right + left) / 2);
if (sortedArr[middle] > value) {
right = middle - 1;
} else if (sortedArr[middle] < value) {
left = middle + 1;
} else {
return middle;
}
}
return -1;
}O(n^2)
function naiveStringSearch(long: string, pattern: string): number {
let count = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < long.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < pattern.length; j++) {
if (pattern[j] !== long[i + j]) {
break;
}
if (j === pattern.length - 1) {
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}array.sort(cb?) will turn all values to string then sort it based on it’s unicode
["a", "c", "b", "f", "d"].sort(); // (5) ["a", "b", "c", "d", "f"]
[1, 10, 6, 8, 2, 3, 5].sort(); //(7) [1, 10, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8]
/*
also receive callback function by two arguments:
a: previous number
b: next number
*/
// if callback return NEGATIVE number a will placed before b
[1, 10, 6, 8, 2, 3, 5].sort((a, b) => a - b); // (7) [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10]
// if callback return POSITIVE number a will placed after b
(7)[(1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10)].sort((a, b) => b - a); // (7) [10, 8, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1]
// if callback return ZERO a and b will placed at the same position
general: O(n^2) nearlySortedData: O(n)
function bubbleSort(arr: number[]): number[] {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
let noSwap = true;
for (let j = 0; j < arr.length - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
[arr[j], arr[j + 1]] = [arr[j + 1], arr[j]];
noSwap = false;
}
}
if (noSwap) break;
}
return arr;
}
// or
function bubbleSort(arr: number[]): number[] {
for (let i = arr.length; i > 0; i--) {
let noSwap = true;
for (let j = 0; j < i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
[arr[j], arr[j + 1]] = [arr[j + 1], arr[j]];
noSwap = false;
}
}
if (noSwap) break;
}
return arr;
}
O(n^2)
function selectionSort(arr: number[]) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
let min = i;
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[min]) {
min = j;
}
}
if (min !== i) {
[arr[i], arr[min]] = [arr[min], arr[i]];
}
}
return arr;
}
general: O(n^2) nearlySortedData: O(n)
function insertionSort(arr) {
var currentVal;
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
currentVal = arr[i];
for (var j = i - 1; j >= 0 && arr[j] > currentVal; j--) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
}
arr[j + 1] = currentVal;
}
return arr;
}| Algorithm | Time Complexity (Best) | Time Complexity (Average) | Time Complexity (worst) | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bubble sort | O(n) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) | O(1) |
| insertion sort | O(n) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) | O(1) |
| selection sort | O(n^2) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) | O(1) |

O(n Log n)
// merge two sorted array
function merge(arr1: number[], arr2: number[]): number[] {
let result = [];
let i = 0;
let j = 0;
while (i < arr1.length && j < arr2.length) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j]) {
result.push(arr1[i]);
i++;
} else {
result.push(arr2[j]);
j++;
}
}
while (i < arr1.length) {
result.push(arr1[i]);
i++;
}
while (j < arr2.length) {
result.push(arr2[j]);
j++;
}
return result;
}
function mergeSort(arr: number[]): number[] {
if (arr.length <= 1) return arr;
const middle = Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
const left = mergeSort(arr.slice(0, middle));
const right = mergeSort(arr.slice(middle));
return merge(left, right);
}
in following implementation we always assume first item as pivot
general: O(n Log n) sorted: O(n^2)
// place pivot in the right index and return pivot index
function pivot(arr: number[], start = 0, end = arr.length - 1) {
const pivot = arr[start];
let pivotIndex = start;
for (let i = start + 1; i < end; i++) {
if (arr[i] < pivot) {
pivotIndex++;
[arr[pivotIndex], arr[i]] = [arr[i], arr[pivotIndex]];
}
}
[arr[start], arr[pivotIndex]] = [arr[pivotIndex], arr[start]];
}
function quickSort(arr: number[], start = 0, end = arr.length - 1) {
if (left < right) {
const pivot = pivot(arr, start, end);
// left
quickSort(arr, start, pivotIndex - 1);
// right
quickSort(arr, pivotIndex + 1, end);
}
return arr;
}
O(nk) n: the number of items we sorting k: average length of those numbers
// get the actual number at the given index
function getDigit(num: number, i: number): number {
return Math.floor(Math.abs(num) / Math.pow(10, i)) % 10;
}
// get number length
function digitCount(num: number): number {
if (num === 0) return 1;
return Math.floor(Math.log10(Math.abs(num))) + 1;
}
// return number by most length
function mostDigits(arr: number[]): number {
let maxDigits = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
maxDigits = Math.max(maxDigits, digitCount(arr[i]));
}
return maxDigits;
}
function radixSort(arr: number[]): number[] {
let maxDigitCount = mostDigits(arr);
for (let k = 0; k < maxDigitCount; k++) {
let digitBuckets = Array.from({ length: 10 }, () => []);
for (let j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
digitBuckets[getDigit(arr[j], k)].push(arr[j]);
}
arr = [].concat(...digitBuckets);
}
return arr;
}| Algorithm | Time Complexity (Best) | Time Complexity (Average) | Time Complexity (worst) | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| merge sort | O(n Log n) | O(n Log n) | O(n Log n) | O(n) |
| quick sort | O(n Log n) | O(n Log n) | O(n^2) | O(Log n) |
| radix sort | O(nk) | O(nk) | O(nk) | O(n + k) |
| DataStructure | Insertion | Removal | Searching | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singly Linked List | O(1) | bestCase(very beginning): O(1) worstCase(very end): O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Doubly Linked List | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) it is faster than Singly Linked List | O(n) |
| Stack | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Queue | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Binary Search Tree | O( Log n) | - | O(Log n) | - |
| Binary Heap | O( Log n) | O( Log n) | O( n ) | - |
| Hash Tables | O( 1 ) | O( 1 ) | - | O( 1 ) |
class _Node {
constructor(public value: any) {}
public next: _Node | null = null;
}
class SinglyLinkedList {
private _length: number = 0;
private head: _Node | null = null;
private tail: _Node | null = null;
get length() {
return this._length;
}
get print(): null | _Node[] {
if (!this._length) return null;
const arr = [];
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode) {
arr.push(currentNode.value);
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return arr;
}
public push(value: any): SinglyLinkedList {
const node = new _Node(value);
if (!this.head || !this.tail) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = this.head;
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}
this._length += 1;
return this;
}
public pop(): _Node | null {
if (!this.head) return null;
let currentNode = this.head;
if (!currentNode.next) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this._length -= 1;
return currentNode;
}
while (currentNode.next && currentNode.next.next) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
this.tail = currentNode;
this.tail.next = null;
this._length -= 1;
return currentNode.next as _Node;
}
public unShift(value: any): SinglyLinkedList {
const currentHead = this.head;
this.head = new _Node(value);
if (currentHead) {
this.head.next = currentHead;
} else {
this.tail = this.head;
}
this._length += 1;
return this;
}
public shift(): _Node | null {
if (!this.head) return null;
const currentHead = this.head;
this.head = currentHead.next;
this._length -= 1;
if (currentHead === this.tail) this.tail = null;
return currentHead;
}
public get(index: number): _Node | null {
if (index < 0 || index >= this._length) return null;
let currentNode = this.head;
for (let j = 0; j < index; j++) {
if (currentNode && currentNode.next) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
}
return currentNode;
}
public set(index: number, value: any): _Node | null {
const node = this.get(index);
if (node) {
node.value = value;
}
return node;
}
public insert(index: number, value: any): SinglyLinkedList | null {
if (index < 0 || index >= this._length) {
return null;
} else if (index === 0) {
return this.unShift(value);
} else if (index === this._length) {
return this.push(value);
} else {
const prevNode = this.get(index - 1);
if (prevNode) {
const newNode = new _Node(value);
newNode.next = prevNode.next;
prevNode.next = newNode;
this._length += 1;
return this;
}
return prevNode;
}
}
public remove(index: number): _Node | null {
if (index === 0) {
return this.shift();
} else if (index === this._length - 1) {
return this.pop();
} else {
const prevNode = this.get(index - 1);
const currentNode = this.get(index);
if (prevNode && currentNode) {
prevNode.next = currentNode.next;
this._length -= 1;
}
return currentNode;
}
}
public reverse(): SinglyLinkedList | false {
if (this._length <= 1) return false;
let node = this.head;
this.head = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
let next: _Node | null;
let prev: _Node | null = null;
for (let i = 0; i < this._length; i++) {
if (node) {
next = node.next;
node.next = prev;
prev = node;
node = next;
}
}
return this;
}
}class _Node {
public next: _Node | null = null;
public prev: _Node | null = null;
constructor(public value: any) {}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
private head: _Node | null = null;
private tail: _Node | null = null;
private _length = 0;
get length() {
return this._length;
}
get print(): null | _Node[] {
if (!this._length) return null;
const arr = [];
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode) {
arr.push(currentNode.value);
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return arr;
}
public push(value: any): DoublyLinkedList {
const node = new _Node(value);
if (!this.tail) {
this.head = node;
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
}
this._length += 1;
this.tail = node;
return this;
}
public pop(): _Node | null {
if (!this.tail) {
return null;
}
const currentTail = this.tail;
if (currentTail.prev) {
this.tail = currentTail.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
currentTail.prev = null;
} else {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
this._length -= 1;
return currentTail;
}
public shift(): null | _Node {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
const currentHead = this.head;
if (currentHead.next) {
this.head = currentHead.next;
this.head.prev = null;
currentHead.next = null;
} else {
return this.pop();
}
this._length -= 1;
return currentHead;
}
public unshift(value: any): DoublyLinkedList {
if (!this.head) {
return this.push(value);
}
const node = new _Node(value);
const currentHead = this.head;
this.head = node;
this.head.next = currentHead;
currentHead.prev = this.head;
this._length += 1;
return this;
}
public get(index: number): null | _Node {
if (index < 0 || index >= this._length) return null;
let currentNode: _Node | null = null;
if (index < Math.floor(this._length / 2)) {
// iterate from head to tail
currentNode = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
if (currentNode && currentNode.next) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
}
} else {
// iterate from tail to head
currentNode = this.tail;
for (let i = this._length - 1; i > index; i--) {
if (currentNode && currentNode.prev) {
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
}
return currentNode;
}
}
return currentNode;
}
public set(index: number, value: any): _Node | null {
const node = this.get(index);
if (node) {
node.value = value;
}
return node;
}
public insert(index: number, value: any): DoublyLinkedList | null {
if (index < 0 || index > this._length) {
return null;
} else if (index === 0) {
return this.unshift(value);
} else if (index === this._length) {
return this.push(value);
} else {
const prevNode = this.get(index - 1);
const nextNode = this.get(index);
if (prevNode && nextNode) {
const newNode = new _Node(value);
prevNode.next = newNode;
(newNode.prev = prevNode), (newNode.next = nextNode);
nextNode.prev = newNode;
}
}
this._length += 1;
return this;
}
public remove(index: number): DoublyLinkedList | null {
if (index < 0 || index > this._length) {
return null;
} else if (index === 0) {
this.shift();
} else if (index === this._length - 1) {
this.pop();
} else {
const node = this.get(index);
if (node && node.prev && node.next) {
(node.prev.next = node.next), (node.next.prev = node.prev);
(node.next = null), (node.prev = null);
}
this._length -= 1;
}
return this;
}
}LIFO last in first out
// implement stack using array
const stack = [1, 2, 3];
stack.push(4); // [1,2,3,4]
stack.pop(); // [1,2,3]
// stacks just have push and pop
stack.unshift(0); // [0,1,2,3]
stack.shift(); // [1,2,3]// implementing stack using singly linked list
class _Node {
public next: _Node | null = null;
constructor(public value: any) {}
}
class Stack {
private first: _Node | null = null;
private last: _Node | null = null;
private _length = 0;
get length(): number {
return this._length;
}
push(value: any): Stack {
const node = new _Node(value);
const currentFirst = this.first;
(this.first = node), (this.first.next = currentFirst);
if (!currentFirst) {
this.last = node;
}
this._length += 1;
return this;
}
pop(): _Node | null {
const currentFirst = this.first;
if (currentFirst) {
if (this.first === this.last) this.last = currentFirst.next;
this.first = currentFirst.next;
this._length -= 1;
}
return currentFirst;
}
}FIFO first in first out
// implementing queue using array
const q = [];
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.shift(1); // out first items first
// or
q.shift(1);
q.shift(2);
q.pop(); // out first items first// implementing queue using singly linked list
class _Node {
public next: _Node | null = null;
constructor(public value: any) {}
}
class Queue {
private first: _Node | null = null;
private last: _Node | null = null;
private _length = 0;
get length(): number {
return this._length;
}
enqueue(value: any): Queue {
const node = new _Node(value);
if (!this.last) {
(this.first = node), (this.last = node);
} else {
this.last.next = node;
this.last = node;
}
this._length += 1;
return this;
}
dequeue(): _Node | null {
const currentFirst = this.first;
if (currentFirst) {
if (this.first === this.last) this.last = null;
this.first = currentFirst.next;
this._length -= 1;
}
return currentFirst;
}
}class _Node {
constructor(public value: number) {}
public left: _Node | null = null;
public right: _Node | null = null;
}
class BinarySearchTree {
public root: _Node | null = null;
public insert(value: number): BinarySearchTree | null {
const node = new _Node(value);
if (!this.root) {
this.root = node;
} else {
let currentNode: _Node = this.root;
do {
if (value === currentNode.value) return null;
if (value < currentNode.value) {
if (currentNode.left) {
currentNode = currentNode.left;
} else {
currentNode.left = node;
break;
}
} else {
if (currentNode.right) {
currentNode = currentNode.right;
} else {
currentNode.right = node;
break;
}
}
} while (currentNode);
}
return this;
}
public have(value: number): boolean {
let currentNode = this.root;
while (currentNode) {
if (value === currentNode.value) {
return true;
} else {
if (value < currentNode.value) {
if (currentNode.left) {
currentNode = currentNode.left;
continue;
}
break;
} else {
if (currentNode.right) {
currentNode = currentNode.right;
continue;
}
break;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}there is two main strategies to traversal a tree : Breadth-first-search and Depth-first-search
class _Node {
constructor(public value: number) {}
public left: _Node | null = null;
public right: _Node | null = null;
}
class BinarySearchTree {
public root: _Node | null = null;
public insert(value: number): BinarySearchTree | null {
const node = new _Node(value);
if (!this.root) {
this.root = node;
} else {
let currentNode: _Node = this.root;
do {
if (value === currentNode.value) return null;
if (value < currentNode.value) {
if (currentNode.left) {
currentNode = currentNode.left;
} else {
currentNode.left = node;
break;
}
} else {
if (currentNode.right) {
currentNode = currentNode.right;
} else {
currentNode.right = node;
break;
}
}
} while (currentNode);
}
return this;
}
public have(value: number): boolean {
let currentNode = this.root;
while (currentNode) {
if (value === currentNode.value) {
return true;
} else {
if (value < currentNode.value) {
if (currentNode.left) {
currentNode = currentNode.left;
}
break;
} else {
if (currentNode.right) {
currentNode = currentNode.right;
continue;
}
break;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/*
breadth first search (bfs) : traverse tree horizontally
*/
public bfs(): _Node[] {
const visited: _Node[] = [];
if (this.root) {
const q: _Node[] = [this.root];
while (q.length) {
if (q[0].left) q.push(q[0].left);
if (q[0].right) q.push(q[0].right);
visited.push(q[0]), q.shift();
}
}
return visited;
}
/*
depth first search (dfs) : traverse tree vertically
following contains three dfs searching methods:
1. preOrder : add node => going to left and add left => going to right and add right
2. postOrder : going to left and add left => going to right and add right => going to node and add node
3. inOrder : going to the left and add left => add node => going to the right and add right
*/
public dfsPreOrder(): _Node[] {
const visited: _Node[] = [];
if (this.root) {
(function traverse(node: _Node): void {
visited.push(node);
if (node.left) {
traverse(node.left);
}
if (node.right) {
traverse(node.right);
}
})(this.root);
}
return visited;
}
public dfsPostOrder(): _Node[] {
const visited: _Node[] = [];
if (this.root) {
(function traverse(node: _Node): void {
if (node.left) {
traverse(node.left);
}
if (node.right) {
traverse(node.right);
}
visited.push(node);
})(this.root);
}
return visited;
}
dfsInOrder(): _Node[] {
const visited: _Node[] = [];
if (this.root) {
(function traverse(node: _Node) {
if (node.left) {
traverse(node.left);
}
visited.push(node);
f;
if (node.right) {
traverse(node.right);
}
})(this.root);
}
return visited;
}
}depth-first vs breadth-first : they both timeComplexity is same but spaceComplexity is different if we got a wide tree like this:

breadth-first take up more space. cuz we adding more element to queue.
if we got a depth long tree like this:

depth-first take up more space.
potentially use cases for dfs variants (preOder postOrder inOrder) preOrder is useful when we want a clone of tree. inOrder is useful when we want data in order that it’s stored in tree.
Max Binary Heap:
Min Binary Heap:

class MaxBinaryHeap {
private _values: number[] = [];
get values(): number[] {
return this._values;
}
private sinkingUp(value: number): void {
let valueIndex = this._values.length - 1;
while (valueIndex > 0) {
const parentIndex = Math.floor((valueIndex - 1) / 2);
const parent = this._values[parentIndex];
if (value <= parent) break;
this._values[parentIndex] = value;
this._values[valueIndex] = parent;
valueIndex = parentIndex;
}
}
private sinkingDown(): void {
let targetIndex = 0;
while (true) {
let leftChildIndex = targetIndex * 2 + 1,
rightChildIndex = targetIndex * 2 + 2;
let target = this._values[targetIndex],
leftChild = this._values[leftChildIndex],
rightChild = this._values[rightChildIndex];
if (target < leftChild && target < rightChild) {
if (rightChild > leftChild) {
[
this._values[targetIndex],
this._values[rightChildIndex]
] = [
this._values[rightChildIndex],
this._values[targetIndex]
];
targetIndex = rightChildIndex;
} else {
[
this._values[targetIndex],
this._values[leftChildIndex]
] = [
this._values[leftChildIndex],
this._values[targetIndex]
];
targetIndex = leftChildIndex;
}
continue;
} else if (rightChild >= target) {
[this._values[targetIndex], this._values[rightChildIndex]] = [
this._values[rightChildIndex],
this._values[targetIndex]
];
targetIndex = leftChildIndex;
continue;
} else if (leftChild >= target) {
[this._values[targetIndex], this._values[leftChildIndex]] = [
this._values[leftChildIndex],
this._values[targetIndex]
];
targetIndex = leftChildIndex;
continue;
}
break;
}
}
public insert(value: number): number[] {
this._values.push(value);
this.sinkingUp(value);
return this._values;
}
public extractMax(): number | null {
if (!this._values.length) {
return null;
}
const root = this._values[0];
this._values[0] = this._values[this._values.length - 1];
this._values.pop();
this.sinkingDown();
return root;
}
}A data structure which every element has a priority. Elements with higher priorities are served before elements with lower priorities.
In the following example, we implemented a priority queue using minBinaryHeap but you should know binaryHeaps and priority queue is two different concepts and we just use an abstract of it
interface INode {
value: any;
priority: number;
}
class _Node implements INode {
constructor(public value: any, public priority: number = 0) {}
}
class PriorityQueue {
private _values: INode[] = [];
get values(): INode[] {
return this._values;
}
private sinkingUp(node: INode): void {
let valueIndex = this._values.length - 1;
while (valueIndex > 0) {
const parentIndex = Math.floor((valueIndex - 1) / 2);
const parent = this._values[parentIndex];
if (node.priority >= parent.priority) break;
this._values[parentIndex] = node;
this._values[valueIndex] = parent;
valueIndex = parentIndex;
}
}
private sinkingDown(): void {
let targetIndex = 0;
while (true) {
let leftChildIndex = targetIndex * 2 + 1,
rightChildIndex = targetIndex * 2 + 2;
let target = this._values[targetIndex],
leftChild = this._values[leftChildIndex],
rightChild = this._values[rightChildIndex];
if (
leftChild &&
rightChild &&
target.priority > leftChild.priority &&
target.priority > rightChild.priority
) {
if (rightChild.priority < leftChild.priority) {
[
this._values[targetIndex],
this._values[rightChildIndex]
] = [
this._values[rightChildIndex],
this._values[targetIndex]
];
targetIndex = rightChildIndex;
} else {
[
this._values[targetIndex],
this._values[leftChildIndex]
] = [
this._values[leftChildIndex],
this._values[targetIndex]
];
targetIndex = leftChildIndex;
}
continue;
} else if (rightChild && rightChild.priority <= target.priority) {
[this._values[targetIndex], this._values[rightChildIndex]] = [
this._values[rightChildIndex],
this._values[targetIndex]
];
targetIndex = leftChildIndex;
continue;
} else if (leftChild && leftChild.priority <= target.priority) {
[this._values[targetIndex], this._values[leftChildIndex]] = [
this._values[leftChildIndex],
this._values[targetIndex]
];
targetIndex = leftChildIndex;
continue;
}
break;
}
}
public enqueue({ value, priority }: INode): _Node[] {
const node = new _Node(value, priority);
this._values.push(node);
this.sinkingUp(node);
return this._values;
}
public dequeue(): _Node | null {
if (!this._values.length) {
return null;
}
const root = this._values[0];
this._values[0] = this._values[this._values.length - 1];
this._values.pop();
this.sinkingDown();
return root;
}
}Hash tables are collection of key-value pairs
There is possibility for handle collisions is hash tables :
type El = [string, any];
class HashTable {
private keyMap: El[][];
constructor(size: number = 53) {
this.keyMap = new Array(size);
}
public _hash(key: string): number {
let total = 0;
const WEIRD_PRIME = 31;
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
const characterCode = key.charCodeAt(i) - 96;
total = (total + characterCode * WEIRD_PRIME) % this.keyMap.length;
}
return total;
}
set(key: string, value: any): El[][] {
const index = this._hash(key);
if (!this.keyMap[index]) {
this.keyMap[index] = [];
}
this.keyMap[index].push([key, value]);
return this.keyMap;
}
get(key: string): El | undefined {
const index = this._hash(key);
const elements = this.keyMap[index];
if (elements) {
for (let value of elements) {
if (value[0] === key) return value[1];
}
}
return undefined;
}
get keys(): string[] {
const keys: string[] = [];
for (let value of this.keyMap) {
if (value) {
for (let _value of value) {
keys.push(_value[0]);
}
}
}
return keys;
}
get values(): any[] {
const values = new Set<any>();
for (let value of this.keyMap) {
if (value) {
for (let _value of value) {
values.add(value[1]);
}
}
}
return [...values];
}
}A graph data structure consists of a finite (and possibly mutable) set of vertices or nodes or points, together with a set of unordered pairs of these vertices for an undirected graph or a set of ordered pairs for directed graph.
vertex :node
edge : connection between nodes
directed/ undirected graph: in directed graph there is a direction assigned to vertices an in undirected no
direction assigned. 
weighted/ unweighted graph: in weighted graph there is a weight associated by edges but in unweighted graph no
weight assigned to edges 


| Operation | Adjacency List | Adjacency Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Add vertex | O(1) | O(V^2) |
| Add Edge | O(1) | O(1) |
| Remove vertex | O(V+E) | O(V^2) |
| Remove Edge | O(E) | O(1) |
| Query | O(V+E) | O(1) |
| Storage | O(V+E) | O(V^2) |
interface AdjacencyList {
[vertex: string]: string[];
}
class Graph {
private _adjacencyList: AdjacencyList = {};
public get adjacencyList(): AdjacencyList {
return this._adjacencyList;
}
public set adjacencyList(value: AdjacencyList) {
this._adjacencyList = value;
}
public addVertex(vertex: string): AdjacencyList {
this._adjacencyList[vertex] = [];
return this._adjacencyList;
}
public addEdge(vertex1: string, vertex2: string): boolean {
if (this._adjacencyList[vertex1] && this._adjacencyList[vertex2]) {
this._adjacencyList[vertex1].push(vertex2),
this._adjacencyList[vertex2].push(vertex1);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public removeEdge(vertex1: string, vertex2: string): boolean {
if (this._adjacencyList[vertex1] && this._adjacencyList[vertex2]) {
(this._adjacencyList[vertex1] = this._adjacencyList[vertex1].filter(
(value: string) => value !== vertex2
)),
(this._adjacencyList[vertex2] = this._adjacencyList[
vertex2
].filter((value: string) => value !== vertex1));
return true;
}
return false;
}
public removeVertex(vertex: string): string | undefined {
if (this._adjacencyList[vertex]) {
for (let key in this._adjacencyList) {
this.removeEdge(key, vertex);
}
delete this._adjacencyList[vertex];
return vertex;
}
return undefined;
}
}interface AdjacencyList {
[vertex: string]: string[];
}
class Graph {
private _adjacencyList: AdjacencyList = {};
public get adjacencyList(): AdjacencyList {
return this._adjacencyList;
}
public set adjacencyList(value: AdjacencyList) {
this._adjacencyList = value;
}
public addVertex(vertex: string): AdjacencyList {
this._adjacencyList[vertex] = [];
return this._adjacencyList;
}
public addEdge(vertex1: string, vertex2: string): boolean {
if (this._adjacencyList[vertex1] && this._adjacencyList[vertex2]) {
this._adjacencyList[vertex1].push(vertex2),
this._adjacencyList[vertex2].push(vertex1);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public removeEdge(vertex1: string, vertex2: string): boolean {
if (this._adjacencyList[vertex1] && this._adjacencyList[vertex2]) {
(this._adjacencyList[vertex1] = this._adjacencyList[vertex1].filter(
(value: string) => value !== vertex2
)),
(this._adjacencyList[vertex2] = this._adjacencyList[
vertex2
].filter((value: string) => value !== vertex1));
return true;
}
return false;
}
public removeVertex(vertex: string): string | undefined {
if (this._adjacencyList[vertex]) {
for (let key in this._adjacencyList) {
this.removeEdge(key, vertex);
}
delete this._adjacencyList[vertex];
return vertex;
}
return undefined;
}
public dfcRecursive(startingVertex: string): string[] {
const results: string[] = [];
const adjacencyList = this._adjacencyList;
let currentVertex = this._adjacencyList[startingVertex];
if (currentVertex) {
const visitedVertex: { [vertex: string]: boolean } = {};
(function traverse(vertex: string | undefined): void {
if (!vertex) return;
if (!visitedVertex[vertex]) {
visitedVertex[vertex] = true;
results.push(vertex);
for (let neighbor of currentVertex) {
if (!visitedVertex[neighbor]) {
currentVertex = adjacencyList[neighbor];
traverse(neighbor);
}
}
}
})(startingVertex);
}
return results;
}
// or
public dfsIterative(startingVertex: string): string[] {
const results: string[] = [];
if (this._adjacencyList[startingVertex]) {
let stack: string[] = [startingVertex];
const visitedVertex: { [vertex: string]: boolean } = {};
while (stack.length) {
debugger;
const currentVertex = stack.pop();
if (currentVertex && !visitedVertex[currentVertex]) {
visitedVertex[currentVertex] = true;
results.push(currentVertex);
stack = [...stack, ...this._adjacencyList[currentVertex]];
}
}
}
return results;
}
public breadthFirstSearch(startingVertex: string): string[] {
const results: string[] = [];
if (this._adjacencyList[startingVertex]) {
let queue = [startingVertex];
const visitedVertex: { [vertex: string]: boolean } = {};
while (queue.length) {
const currentVertex = queue.shift();
if (currentVertex && !visitedVertex[currentVertex]) {
visitedVertex[currentVertex] = true;
results.push(currentVertex);
queue = [...queue, ...this._adjacencyList[currentVertex]];
}
}
}
return results;
}
}Finding shortest path between two vertices in a weighted graph.

interface Value {
value: any;
priority: number;
}
interface Neighbor {
vertex: string;
weight: number;
}
interface AdjacencyList {
[vertex: string]: Neighbor[];
}
// naive priority queue
class PriorityQueue {
private _values: Value[] = [];
public get values(): Value[] {
return this._values;
}
public enqueue(value: any, priority: number): Value[] {
this._values.push({ value, priority });
this.sort();
return this._values;
}
public dequeue(): Value {
const value = this._values.shift();
return value as Value;
}
private sort() {
this._values.sort((a: Value, b: Value) => a.priority - b.priority);
}
}
class WeightedGraph {
private _adjacencyList: AdjacencyList = {};
public get adjacencyList(): AdjacencyList {
return this._adjacencyList;
}
public set adjacencyList(value: AdjacencyList) {
this._adjacencyList = value;
}
public addVertex(vertex: string): AdjacencyList {
this._adjacencyList[vertex] = [];
return this._adjacencyList;
}
public addEdge(vertex1: string, vertex2: string, weight: number): boolean {
if (this._adjacencyList[vertex1]) {
this._adjacencyList[vertex1].push({ vertex: vertex2, weight });
this._adjacencyList[vertex2].push({ vertex: vertex1, weight });
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*
dijkstra shortest path first
*/
dijkstraSPF(startingVertex: string, targetVertex: string): string[] {
let path: string[] = [];
if (
this._adjacencyList[startingVertex] &&
this._adjacencyList[targetVertex]
) {
const pq = new PriorityQueue();
const previousVertex: { [vertex: string]: string | null } = {};
const distances: { [vertex: string]: number } = {};
// build initial states
for (let key in this._adjacencyList) {
if (key === startingVertex) {
(distances[key] = 0), pq.enqueue(key, 0);
} else {
distances[key] = Infinity;
pq.enqueue(key, Infinity);
}
previousVertex[key] = null;
}
while (pq.values.length) {
let smallest = pq.dequeue().value;
if (smallest) {
if (smallest === targetVertex) {
// done build path
while (
previousVertex[smallest] ||
smallest === startingVertex
) {
path.push(smallest);
smallest = previousVertex[smallest];
}
break;
}
for (let neighbor of this._adjacencyList[smallest]) {
const candidate = distances[smallest] + neighbor.weight;
let nextNeighbor = neighbor.vertex;
if (candidate < distances[nextNeighbor]) {
distances[nextNeighbor] = candidate;
previousVertex[nextNeighbor] = smallest;
pq.enqueue(nextNeighbor, candidate);
}
}
}
}
}
return path.reverse();
}
}It’s a method for solving a complex problems by breaking it down into a collection of simpler problems, solving their subProblems once and storing their solutions. technically it using knowledge of last problems to solve next by memorization
Let’s implement it without dynamic programming:without dynamic programming:
in fibonacci sequence fib(n) = fib(n-2) + fib(n-1) && fin(1) = 1 && fib(2) = 1
O(2^n)

As you see we calculate f(5) two times with current implementation.
Storing the results of expensive function class and returning the cached result when the same inputs occur again.
O(n)
function fib(n: number, memo: number[] = []): number {
if (memo[n]) return memo[n];
if (n <= 2) return 1;
const res = fib(n - 1, memo) + fib(n - 2, memo);
memo[n] = res;
return res;
}
fib(10000); // Maximum callStack exceededfunction fib(n: number): number {
if (n <= 2) return 1;
const fibNumbers = [0, 1, 1];
for (let index = 3; index <= n; index++) {
fibNumbers[index] = fibNumbers[index - 1] + fibNumbers[index - 2];
}
console.log(fibNumbers);
return fibNumbers[n];
}
fib(10000); // Infinity// turn it to boolean
console.log(!!1); // true
console.log(!!0); // false
// group operation
(newNode.prev = prevNode), (newNode.next = nextNode);// regex.test(str: number) Returns a Boolean value that indicates whether or not a pattern exists in a searched string.
function charCount(str: string) {
const result: { [key: string]: number } = {};
for (let char of str) {
char = char.toLowerCase();
if (/[a-z0-9]/.test(char)) {
result[char] = ++result[char] || 1;
}
}
return result;
}
// *** string.chatCodeAt(i: number) Returns the unicode of value on specified location
/*
numeric (0-9) code > 47 && code < 58;
upper alpha (A-Z) code > 64 && code < 91;
lower alpha (a-z) code > 96 && code <123;
*/
function charCount(str: string) {
const result: { [key: string]: number } = {};
for (let char of str) {
if (isAlphaNumeric(char)) {
char = char.toLowerCase();
result[char] = ++result[char] || 1;
}
}
return result;
}
function isAlphaNumeric(char: string) {
const code = char.charCodeAt(0);
if (
!(code > 47 && code < 58) &&
!(code > 64 && code < 91) &&
!(code > 96 && code < 123)
) {
return false;
}
return true;
}const array = ["hello", "world"];
arr.find(el => el === "world"); // world
arr.findIndex(el => el === "world"); // 1
[1, 2].includes(1); // true
Array.from({ length: 2 }, () => ["lol"]); // [["lol"], ["lol"]]
const stack = ["A", "B", "D", "E", "C", "F"];
const s = stack.shift();
const p = stack.pop();
console.log(s); // "A"
console.log(p); // "F"
["a", "b"].reverse(); // ['b', 'a']delete this._adjacencyList[vertex]; // delete key and value from object
delete this._adjacencyList.vertex;const map = new Map();
// store any type of **unique key** of use duplicate key it will override last value
map.set({ 1: "Object" }, "Object");
map.set(["arr"], "arr");
map.set(1, "number");
map.set(false, "boolean");
map.set(() => console.log("Function"), "Function");
console.log(map);
/*
0: {Object => "Object"}
1: {Array(1) => "arr"}
2: {1 => "number"}
3: {false => "boolean"}
4: {function () { return console.log("Function"); } => "Function"}
*/
// iterable by **for (let [key, value] of map)**
for (let [key, value] of map) console.log(key, value);
// map to arr
const arr = [...map]; // :[ [key, value] ]
/*
0: (2) [{…}, "Object"]
1: (2) [Array(1), "arr"]
2: (2) [1, "number"]
3: (2) [false, "boolean"]
4: (2) [ƒ, "Function"]
*/