

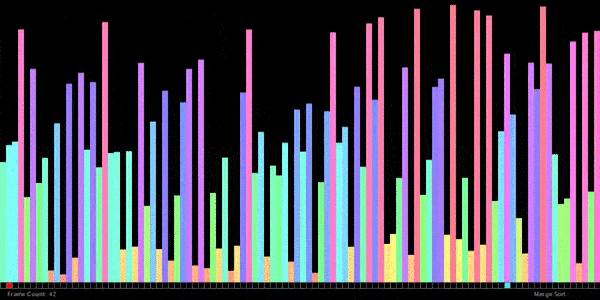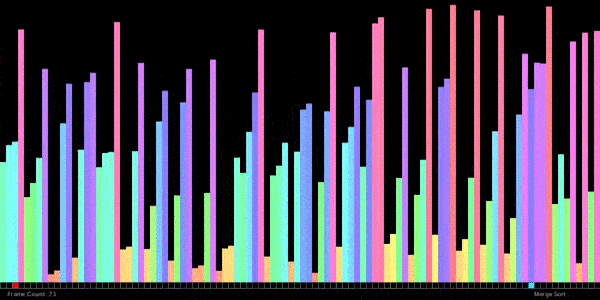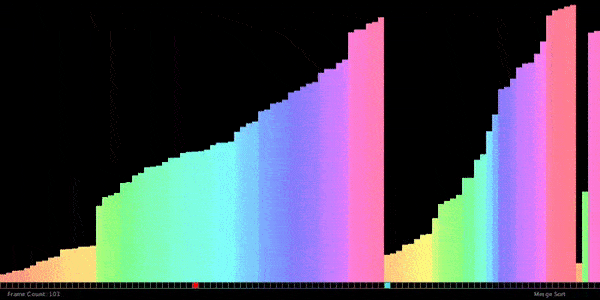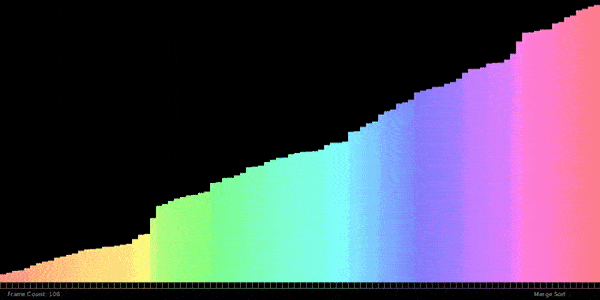

// ——————————————————————————————————————–
Guess What Algo
// ——————————————————————————————————————–
<===================~~==-----==()==-----==~~==========================>
// HINTS:
// divide and conquer // need a helper function that solves merging elements of two sorted arrays into a single sorted array
function guessWhatAlgo(array) {
if (array.length <= 1) {
return array;
}
let midIdx = Math.floor(array.length / 2);
let leftHalf = array.slice(0, midIdx);
let rightHalf = array.slice(midIdx);
let sortedLeft = guessWhatAlgo(leftHalf);
let sortedRight = guessWhatAlgo(rightHalf);
return helperguessWhatAlgo(sortedLeft, sortedRight);
}// ANSWER: Merge sort
// if there is only one element in the list, it is already sorted.return that array. // otherwise, divide the list recursively into two halves until it can no more be divided. // merge the smaller lists into new list in sorted order.
// TIME COMPLEXITY: O(nlogn)
// SPACE COMPLEXITY:O(n) 




<===================~~==-----==()==-----==~~==========================>

 // HINT:
// HINT:
// works by performing multiple passes to move elements closer to their final positions
function guessWhatAlgo(array) {
let swapped = true;
while (swapped) {
// O(n)
swapped = false;
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
//O(n)
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
swap(array, i, i + 1);
swapped = true;
}
}
}
return array;
}// ANSWER: Bubble sort
// TIME COMPLEXITY: O(n * n === n^2)
// SPACE COMPLEXITY: O(1) 


<===================~~==-----==()==-----==~~==========================>
// HINT:
function guessWhatAlgo(array) {
if (array.length <= 1) {
return array;
}
let pivot = array.shift();
let left = array.filter((el) => el < pivot);
let right = array.filter((el) => el >= pivot);
let leftSorted = guessWhatAlgo(left);
let rightSorted = guessWhatAlgo(right);
return [...leftSorted, pivot, ...rightSorted];
}// ANSWER: Quick sort
// TIME COMPLEXITY: worst case: O(n^2) best case: O(nlogn)
// SPACE COMPLEXITY:O(n) 


<===================~~==-----==()==-----==~~==========================>
function guessWhatAlgo(arr) {
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
let currElement = arr[i];
for (var j = i - 1; j >= 0 && currElement < arr[j]; j--) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
}
arr[j + 1] = currElement;
}
return arr;
}// ANSWER: Insertion sort
// TIME COMPLEXITY: O(n^2)
// SPACE COMPLEXITY:O(1)



<===================~~==-----==()==-----==~~==========================>
function guessWhatAlgo(array, target) {
if (array.length === 0) {
return false;
}
let midIdx = Math.floor(array.length / 2);
if (target < array[midIdx]) {
let leftHalf = array.slice(0, midIdx);
return guessWhatAlgo(leftHalf, target);
} else if (target > array[midIdx]) {
let rightHalf = array.slice(midIdx + 1);
return guessWhatAlgo(rightHalf, target);
} else {
return true;
}
}// ANSWER: Binary Search
// TIME COMPLEXITY: O(logn)
// SPACE COMPLEXITY:O(n) 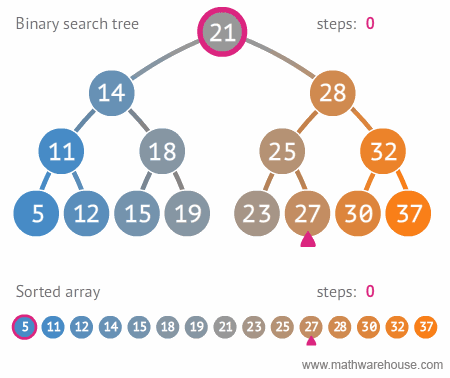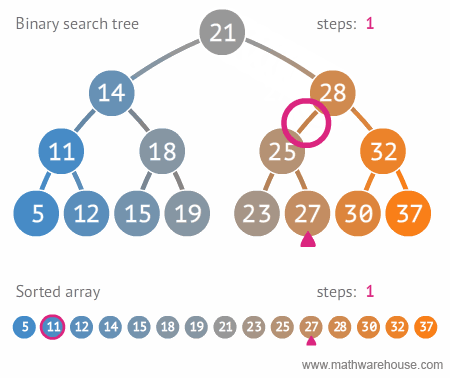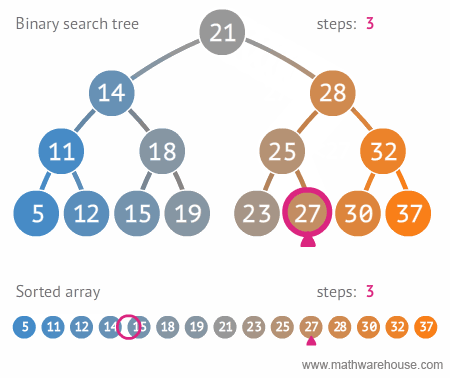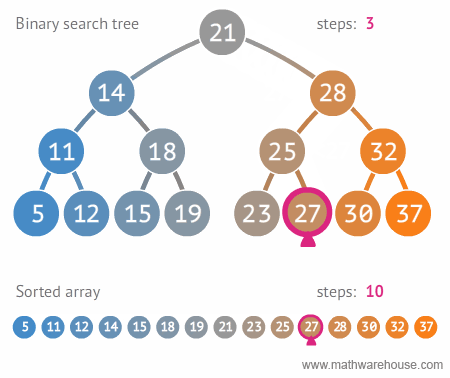
 ]
]
<===================~~==-----==()==-----==~~==========================>
function guessWhatAlgo(arr) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
let minIndex = i;
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[minIndex] > arr[j]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
swap(arr, i, minIndex);
}
return arr;
}// ANSWER: Selection sort
// TIME COMPLEXITY: O(n^2)
// SPACE COMPLEXITY:O(1)



// Use this pseudocode to implement the bubble sort function bubbleSort(array) { // n := length(array) // repeat // swapped = false // for i := 1 to n - 1 inclusive do // // /* if this pair is out of order / // if A[i - 1] > A[i] then // // / swap them and remember something changed */ // swap(A[i - 1], A[i]) // swapped := true // // end if // end for // until not swapped }
function swap(array, idx1, idx2) {
let temp = array[idx1]; // save a copy of the first value
array[idx1] = array[idx2]; // overwrite the first value with the second value
array[idx2] = temp; // overwrite the second value with the first value
}function bubbleSort(array) {
// this variable will be used to track whether or not we
// made a swap on the previous pass. If we did not make
// any swap on the previous pass, then the array must
// already be sorted
let swapped = true;
// this while will keep doing passes if a swap was made
// on the previous pass
while (swapped) {
swapped = false; // reset swap to false
// this for will perform a single pass
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
// if the two value are not ordered...
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
// swap the two values
swap(array, i, i + 1);
// since you made a swap, remember that you did so
// b/c we should perform another pass after this one
swapped = true;
}
}
}
return array;
}// Try to implement swap on your own, this time.
function swap(arr, index1, index2) {}
function selectionSort(list) {
// list : array of items
// n : size of list
//
// for i = 1 to n - 1
// /* set current element as minimum*/
// min = i
//
// /* check the element to be minimum */
//
// for j = i+1 to n
// if list[j] < list[min] then
// min = j;
// end if
// end for
//
// /* swap the minimum element with the current element
// using the above swap function*/
// if indexMin != i then
// swap list[min] and list[i]
// end if
// end for
}
function selectionSort(arr) {
// the `i` loop will track the index that points to the first element of the unsorted region:
// this means that the sorted region is everything left of index i
// and the unsorted region is everything to the right of index i
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
let minIndex = i;
// the `j` loop will iterate through the unsorted region and find the index of the smallest element
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[minIndex] > arr[j]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
// after we find the minIndex in the unsorted region,
// swap that minIndex with the first index of the unsorted region
swap(arr, i, minIndex);
}
return arr;
}function insertionSort(list) {
// for i from 1 to length(list) inclusive do:
// /* select value to be inserted */
// valueToInsert = list[i]
// holePosition = i
// /* locate hole position for the element to be inserted */
// while holePosition > 0 and list[holePosition-1] > valueToInsert do:
// list[holePosition] = list[holePosition-1]
// holePosition = holePosition -1
// end while
// /* insert the number at hole position */
// list[holePosition] = valueToInsert
// end for
}
// All 3 implementations work the same, just a reworking of syntax
// Insertion sort keeps a sorted left region working from left to right examining
// each item and comparing it to items on its left. It then inserts the item in
// the correct oposition in the array.
function insertionSortV2(arr) {
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
let j = i;
while (j > 0 && arr[j - 1] > arr[j]) {
swap(arr, j - 1, j);
j--;
}
}
return arr;
}
function swap(arr, index1, index2) {
let temp = arr[index1];
arr[index1] = arr[index2];
arr[index2] = temp;
}
// The version below swaps out the for loop for a while loop to avoid using var
function insertionSortV2(arr) {
// the `i` loop will iterate through every element of the array
// we begin at i = 1, because we can consider the first element of the array as a
// trivially sorted region of only one element
// insertion sort allows us to insert new elements anywhere within the sorted region
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
// grab the first element of the unsorted region
let currElement = arr[i];
// the `j` loop will iterate left through the sorted region,
// looking for a legal spot to insert currElement
let j = i - 1;
// keep moving left while currElement is less than the j-th element
while (j >= 0 && currElement < arr[j]) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
// the line above will move the j-th element to the right,
// leaving a gap to potentially insert currElement
// we have to remember to decrement in our while loop!
j--;
}
// insert currElement into that gap
arr[j + 1] = currElement;
}
return arr;
}
// This solution utilizes var in the inner for loop to be able to use the variable
// after the loop exits. I generally try to avoid var because of the complications
// it can present.
function insertionSortV3(arr) {
// the `i` loop will iterate through every element of the array
// we begin at i = 1, because we can consider the first element of the array as a
// trivially sorted region of only one element
// insertion sort allows us to insert new elements anywhere within the sorted region
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
// grab the first element of the unsorted region
let currElement = arr[i];
// the `j` loop will iterate left through the sorted region,
// looking for a legal spot to insert currElement
for (var j = i - 1; j >= 0 && currElement < arr[j]; j--) {
// keep moving left while currElement is less than the j-th element
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
// the line above will move the j-th element to the right,
// leaving a gap to potentially insert currElement
}
// insert currElement into that gap
arr[j + 1] = currElement;
}
return arr;
}
function merge(array1, array2) {
// var result as array
// while ( a and b have elements )
// if ( a[0] > b[0] )
// add b[0] to the end of result
// remove b[0] from b
// else
// add a[0] to the end of result
// remove a[0] from a
// end if
// end while
// while ( a has elements )
// add a[0] to the end of result
// remove a[0] from a
// end while
// while ( b has elements )
// add b[0] to the end of result
// remove b[0] from b
// end while
// return result
}
function mergeSort(array) {
// if ( n == 1 ) return a
// /* Split the array into two */
// var l1 as array = a[0] ... a[n/2]
// var l2 as array = a[n/2+1] ... a[n]
// l1 = mergesort( l1 )
// l2 = mergesort( l2 )
// return merge( l1, l2 )
}
function merge(array1, array2) {
let merged = [];
while (array1.length || array2.length) {
let ele1 = array1.length ? array1[0] : Infinity;
let ele2 = array2.length ? array2[0] : Infinity;
let next;
if (ele1 < ele2) {
next = array1.shift();
} else {
next = array2.shift();
}
merged.push(next);
}
return merged;
}
function mergeSort(array) {
if (array.length <= 1) {
return array;
}
let midIdx = Math.floor(array.length / 2);
let leftHalf = array.slice(0, midIdx);
let rightHalf = array.slice(midIdx);
let sortedLeft = mergeSort(leftHalf);
let sortedRight = mergeSort(rightHalf);
return merge(sortedLeft, sortedRight);
}function quickSort(array) {
// if the length of the array is 0 or 1, return the array
// set the pivot to the first element of the array
// remove the first element of the array
// put all values less than the pivot value into an array called left
// put all values greater than the pivot value into an array called right
// call quick sort on left and assign the return value to leftSorted
// call quick sort on right and assign the return value to rightSorted
// return the concatenation of leftSorted, the pivot value, and rightSorted
}
function quickSort(array) {
if (array.length <= 1) {
return array;
}
let pivot = array.shift();
let left = array.filter((el) => el < pivot);
let right = array.filter((el) => el >= pivot);
let leftSorted = quickSort(left);
let rightSorted = quickSort(right);
return [ ...leftSorted, pivot, ...rightSorted ];
}