Basics
-
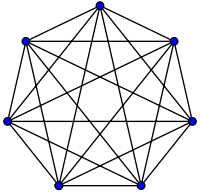
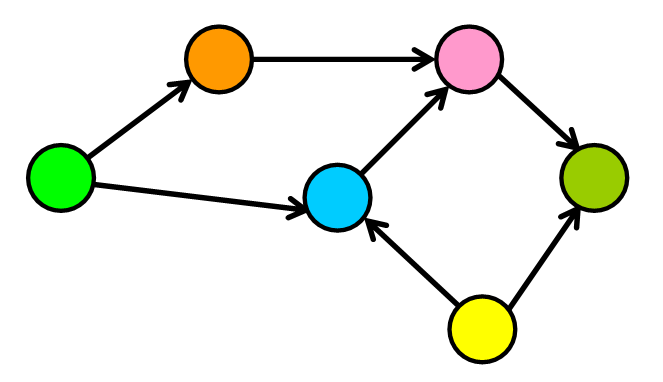
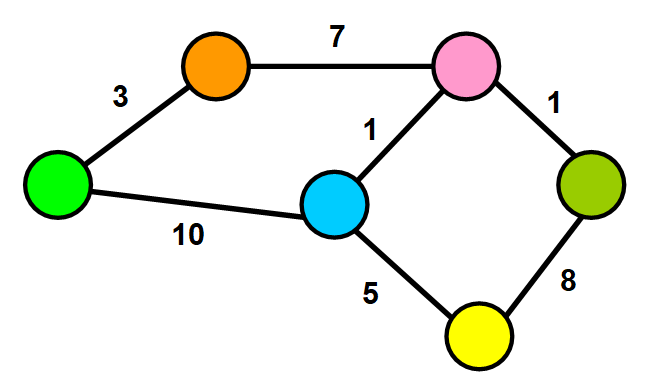
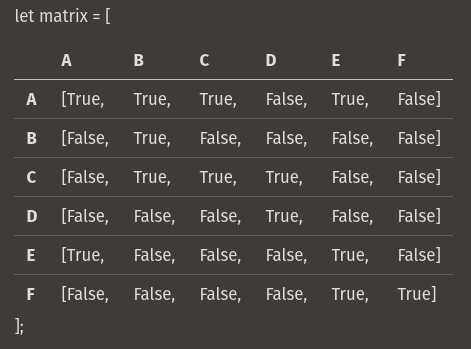
A graph is any collection of nodes and
- Much more relaxed in structure than a tree.
- It doesn't need to have a root node (not every node needs to be accessible from a single node)
-
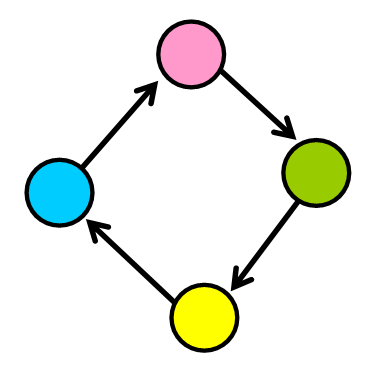
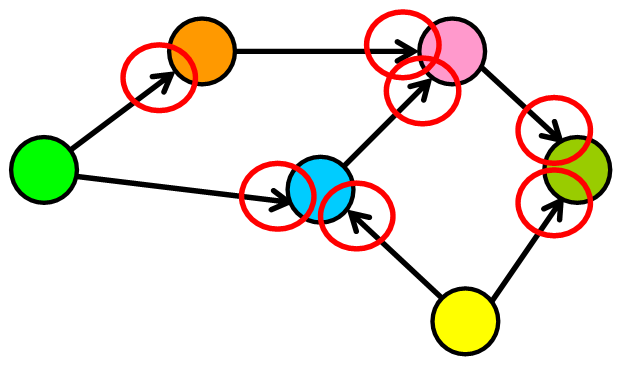
It can have cycles (a group of nodes whose paths begin and end at the
same node)
- Cycles are not always “isolated”, they can be one part of a larger graph. You can detect them by starting your search on a specific node and finding a path that takes you back to that same node.
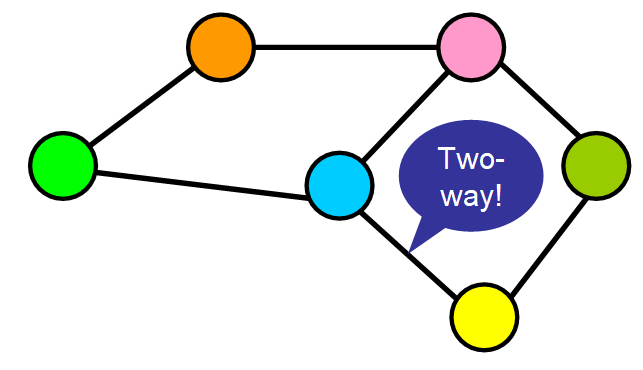
- Any number of edges may leave a given node
- A Path is a sequence of nodes on a graph